Device for Measurements of friction Coefficient and Slidability
Description of the Technology
The principal scheme of a device is shown in the following Fig 1. The device working principle is based on an adjustable inclined plane (poz. 1 in Fig. 1) that is equipped with additional optical sensors (poz. 7 in Fig. 1). The sensors allow to measure time that is necessary for the sample to slide specific distance down the plane.>
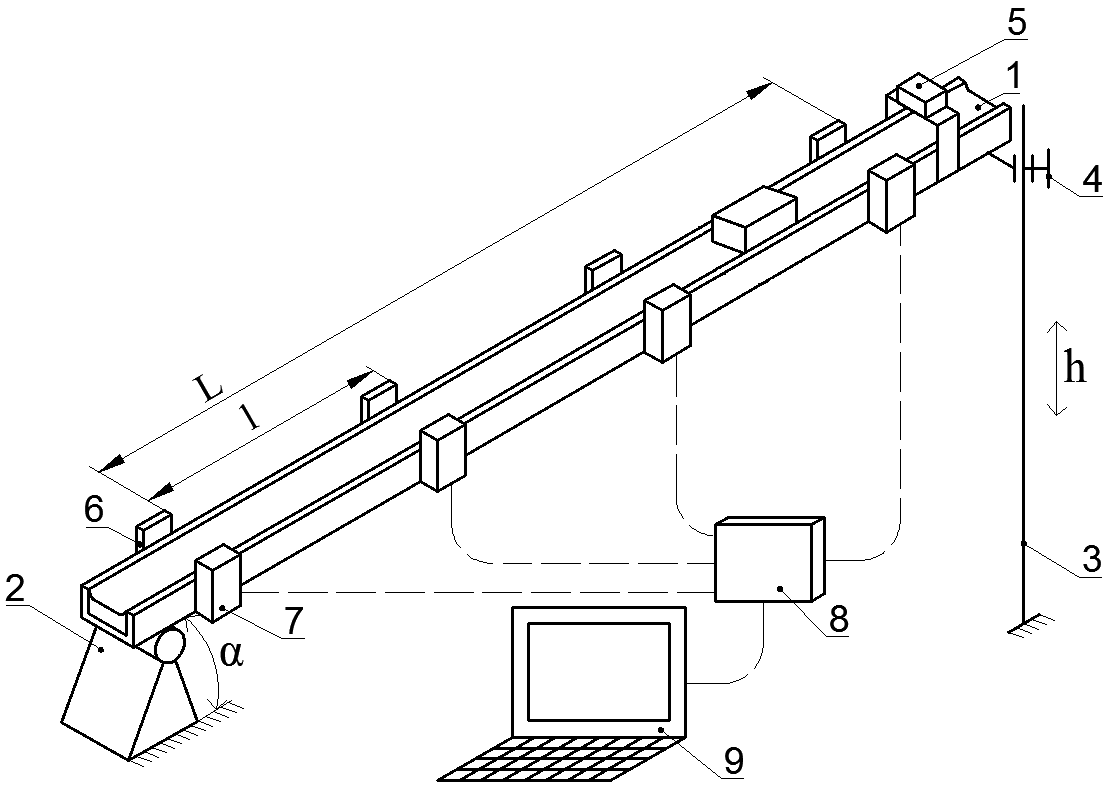
Fig. 1. The principal scheme of the device.
1 – Inclined plane;
2 – Knuckle;
3 – Linear guide;
4 – Fixation screw;
5 – Sample launcher;
6 – Optical sensor;
7 – Optical sensor reflector;
8 – Sensor signal interface;
9 – Personal computer;
L –Total measurement distance;
l – Distance between sensors;
α – Plane angle;
h – Linear guide height.
Device allows to maintain two types of experiments:
- Static friction coefficient measurement if sample is set on horizontally leveled plane and angle α (Fig) is then slowly increased till movement of the sample is detected. Static friction coefficient can be calculated as tangent from the angle at which sample get loose.
- Slidability measurements if samples with same macro geometry and weight are launched from the top of the plane at specific angle α and the time that was necessary for them to slide distance (l) between sensors and to reach the end of the plane (L) is measured. Sliding times can be compared thus allowing to determine which sample has best sliding ability.
Applications
The device can be used for measurements of static friction coefficient and slidability for various material and also for investigation how different surface modifications affects slidability. Some of the most typical applications are: • Two solid material sliding ability in dry friction regime; • Friction reducing coating and lubricant investigation; • Ice friction investigation; • Critical sliding angle determination (useful in fields of roof angle determination so the ice and snow does not stick on it, car tire material test, etc.
Advantages
The devices is made with maximal flexibility regarding to base material alteration, i.e. it is easily to change material plane on which samples afterwards will be slide. If ambient temperature is below 0°C ice plane can be used as friction surface. Also the sliding sample size and weight are not strictly limited, that eases the sample preparation and allows to measure additional weight influence on the sliding process. Optical sensors allow to measure time that is necessary for the sample to slide specific distance down the plane. If the sliding time is compared for samples with same macro geometry and weight one can determine which sample surface modification offers best sliding ability. Four additional sensors allow to understand better sliding process because the sliding velocity can be compared also in waypoints in-between total measurement distance.
The device allows to make ice friction investigation. It can achieve better detection of influence of different parameters on slidability than other measurement methods.
Keywords
Friction coefficient,sliding,slidability,measuring equipment,inclined plane